Unlocking Data’s Potential: How Self-Service Business Intelligence Software Builds Insights
In today’s data-driven world, businesses are drowning in information. The true challenge lies not in collecting data, but in transforming it into actionable insights. This is where self-service business intelligence (BI) software steps in. It empowers users across an organization to analyze data, build reports, and make informed decisions without relying heavily on IT or data science teams. This article explores the power of self-service business intelligence software, examining its benefits, functionalities, and impact on modern business strategies.
The Rise of Self-Service BI
Traditional BI solutions often involved complex processes, specialized skills, and lengthy implementation timelines. Data analysis was typically the domain of a select few, creating bottlenecks and hindering timely decision-making. Self-service business intelligence software has disrupted this model. It democratizes data access, putting the analytical power directly into the hands of business users. This shift is fueled by several factors, including the increasing volume of data, the need for faster insights, and the desire for greater agility in responding to market changes.
The core concept behind self-service BI is simplicity. Software is designed with intuitive interfaces, drag-and-drop functionality, and pre-built templates. This allows users with varying technical skill levels to easily explore data, create visualizations, and generate reports. The focus is on empowering users to answer their own questions, fostering a data-driven culture across the organization.
Key Features and Functionalities of Self-Service BI Software
Self-service business intelligence software offers a wide range of features and functionalities. These tools enable users to perform comprehensive data analysis. Key features include:
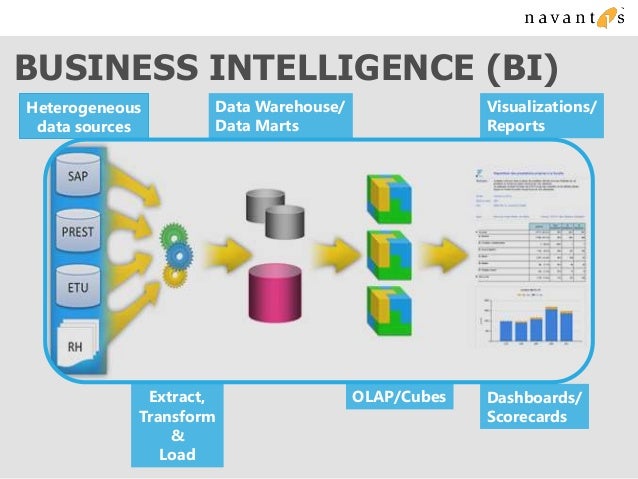
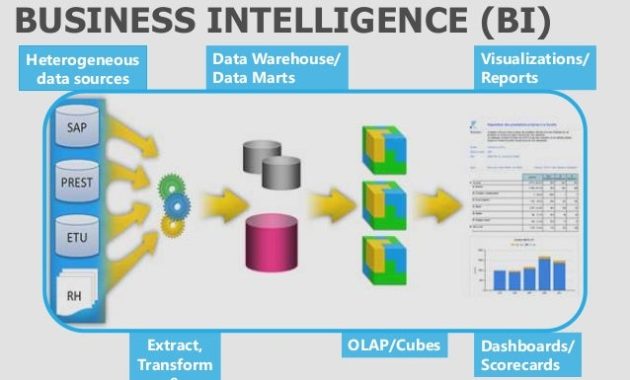
- Data Integration: Connecting to various data sources, including databases, spreadsheets, cloud platforms, and APIs.
- Data Preparation: Cleaning, transforming, and shaping data for analysis. This includes tasks like data cleansing, deduplication, and format conversions.
- Data Visualization: Creating a variety of charts, graphs, and dashboards to present data in an easily understandable format. Common visualizations include bar charts, pie charts, line graphs, and heatmaps.
- Reporting and Dashboards: Designing custom reports and dashboards to track key performance indicators (KPIs) and monitor business performance.
- Data Exploration: Using interactive tools to drill down into data, identify trends, and uncover hidden insights.
- Ad-hoc Analysis: Allowing users to perform on-the-fly analysis, answering specific questions as they arise.
- Collaboration and Sharing: Enabling users to share reports, dashboards, and insights with colleagues, fostering collaboration and knowledge sharing.
- Mobile Access: Providing access to data and insights on mobile devices, enabling users to stay informed on the go.
Benefits of Implementing Self-Service BI
The adoption of self-service business intelligence software offers numerous benefits for organizations. These advantages translate into improved decision-making, increased efficiency, and enhanced competitiveness.
- Faster Decision-Making: By providing quick access to data and insights, self-service BI enables faster and more informed decision-making.
- Improved Data Literacy: Empowering users to work with data increases data literacy across the organization. This fosters a culture of data-driven decision-making.
- Reduced Reliance on IT: Self-service BI reduces the burden on IT departments. Business users can perform their own analysis without requiring IT intervention.
- Increased Efficiency: Automating reporting and analysis tasks frees up valuable time for business users. They can focus on strategic initiatives rather than data manipulation.
- Enhanced Collaboration: Built-in collaboration features facilitate the sharing of insights and promote teamwork.
- Better Business Performance: By identifying trends, opportunities, and risks, self-service BI helps businesses improve performance. It can optimize operations, increase revenue, and reduce costs.
- Cost Savings: By streamlining data analysis and reducing IT workload, self-service BI can lead to significant cost savings.
Choosing the Right Self-Service BI Software
Selecting the right self-service business intelligence software is crucial for maximizing its benefits. Several factors should be considered during the evaluation process:
- Ease of Use: The software should have an intuitive interface and user-friendly features, allowing users of all skill levels to easily navigate and analyze data.
- Data Connectivity: The software should support a wide range of data sources, including databases, cloud platforms, and spreadsheets.
- Data Visualization Capabilities: The software should offer a variety of visualization options to present data effectively.
- Reporting and Dashboarding: The software should allow users to create custom reports and dashboards to track KPIs.
- Scalability: The software should be able to handle growing data volumes and user needs.
- Security: The software should provide robust security features to protect sensitive data.
- Integration: Consider how well the software integrates with existing business systems.
- Pricing and Licensing: Evaluate the pricing model and ensure it aligns with your budget and needs.
- Support and Training: Assess the vendor’s support and training offerings to ensure users have the resources they need to succeed.
Real-World Applications of Self-Service BI
Self-service business intelligence software is used across a wide range of industries and departments. Here are some real-world examples:
- Sales and Marketing: Analyzing sales performance, identifying customer segments, and tracking marketing campaign effectiveness.
- Finance: Monitoring financial performance, creating budgets, and analyzing profitability.
- Operations: Optimizing supply chains, tracking inventory levels, and improving operational efficiency.
- Human Resources: Analyzing employee performance, tracking recruitment metrics, and identifying training needs.
- Healthcare: Monitoring patient outcomes, analyzing healthcare costs, and improving operational efficiency.
- Retail: Analyzing sales data, identifying customer preferences, and optimizing inventory management.
These examples demonstrate the versatility of self-service BI and its ability to address specific business challenges.
Challenges and Considerations
While self-service business intelligence software offers significant advantages, there are also challenges to consider:
- Data Quality: The accuracy and reliability of insights depend on the quality of the underlying data. Organizations must ensure data is clean, consistent, and accurate.
- Data Governance: Implementing data governance policies is essential to ensure data is used responsibly and ethically.
- Training and Adoption: Providing adequate training and support is crucial to ensure users can effectively use the software.
- Data Security: Protecting sensitive data is paramount. Organizations must implement robust security measures.
- Over-Reliance on Data: It is important to avoid over-reliance on data. Qualitative insights and human judgment are also essential for effective decision-making.
The Future of Self-Service BI
The future of self-service business intelligence software is bright. Several trends are shaping its evolution:
- Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML): AI and ML are being integrated into self-service BI platforms. This allows for automated insights, predictive analytics, and intelligent data exploration.
- Cloud-Based BI: Cloud-based self-service BI solutions are becoming increasingly popular. They offer greater flexibility, scalability, and cost-effectiveness.
- Mobile BI: Mobile BI continues to grow in importance, enabling users to access data and insights from anywhere.
- Data Storytelling: The ability to communicate insights effectively is becoming increasingly important. Self-service BI tools are evolving to support data storytelling.
These trends are driving innovation and making self-service BI even more powerful and accessible.
Conclusion: Embracing Data-Driven Decision-Making with Self-Service BI
Self-service business intelligence software has revolutionized the way businesses approach data analysis. By empowering users to explore data and build insights, these tools enable faster decision-making, improved efficiency, and enhanced competitiveness. While there are challenges to consider, the benefits of self-service BI are undeniable. As technology continues to evolve, self-service BI will play an increasingly important role in helping organizations unlock the full potential of their data and achieve their strategic goals. Investing in the right self-service business intelligence software is a crucial step towards building a data-driven culture and driving business success.
[See also: How to Choose the Best BI Tool for Your Business]
[See also: Data Visualization Best Practices for Enhanced Insights]
[See also: The Role of Data Governance in Self-Service BI]